사자자리
[C++] 분할 컴파일: #ifndef & #endif 본문
*Visual Studio 기본 레이아웃 불러오기: 창 - 창 레이아웃 다시 설정
분할 컴파일
- 프로그램을 구성하는 함수들을 별개의 파일에 넣는 것
- 파일들을 개별적으로 컴파일한 후, 하나의 최종 프로그램으로 링크하는 것
//main.cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Profile {
string name;
int age;
};
void display(Profile&);
void display(Profile& temp) {
cout << "이름: " << temp.name << endl;
cout << "나이: " << temp.age << endl;
}
int main() {
Profile RAB = { "Regulus Black", 18 };
display(RAB);
return 0;
}
헤더 파일
1. 함수 원형
2. 기호 상수(#define, const)
3. 인라인 함수
4. 구조체, 클래스, 템플릿 등 선언
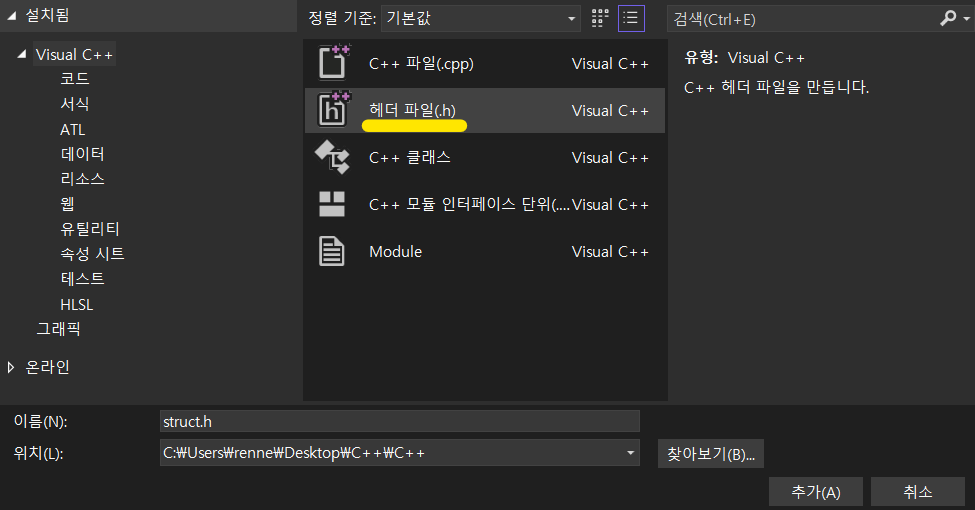
- 헤더 파일 오른쪽 클릭 - 추가 - 새 항목
- 분할 컴파일을 할 때, 하나의 헤더 파일이 여러 cpp 파일에서 중복해서 포함되는 경우가 생긴다.
- 이 때, 중복 include를 막기 위해 ifndef과 endif이 사용된다.
#ifndef & #endif
- if not defined
- 헤더 파일이 정의되어 있지 않는다면, 정의한다.
- 헤더 파일이 이미 정의되어 있다면, #endif를 만나기 전의 모든 코드를 무시한다.
//struct.h
#ifndef STRUCT
#define STRUCT //STRUCT가 main에 포함되기 위해서는 기호 상수로 정의해야 한다.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Profile {
string name;
int age;
};
void display(Profile&);
#endif//main.cpp
#include "struct.h"
int main() {
Profile RAB = { "Regulus Black", 18 };
display(RAB);
return 0;
}//function.cpp
#include "struct.h"
void display(Profile& temp) {
cout << "이름: " << temp.name << endl;
cout << "나이: " << temp.age << endl;
}
'C++ > C++ 이론' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [C++] 클래스 생성자와 소멸자 (0) | 2022.08.17 |
|---|---|
| [C++] 추상화와 클래스 (0) | 2022.08.17 |
| [C++] 함수의 활용 (0) | 2022.08.05 |
| [C++] 함수 (0) | 2022.08.03 |
| [C++] 조건문 if, switch / 논리연산자 (0) | 2022.07.27 |
Comments




