사자자리
[웹기초] 생활코딩 PHP 18 ~ PHP 30 본문
https://www.php.net/manual/en/functions.user-defined.php
PHP: User-defined functions - Manual
";echo $b;}$x = "Foo";$y = "Bar";$z = "Baz";myName1($x,$y,$z);echo " ";function myName2($b="John",...$a){print_r($a);echo " ";echo $b;}$x = "Foo";$y = "Bar";$z = "Baz";myName2($x,$y,$z);echo " ";?>
www.php.net
사용자 정의 함수
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<?php
function basic(){ //인수를 받지 않는 함수
print("This is Basic.<br>");
}
basic();
function sum($x, $y){ //인수를 받는 함수
print($x + $y);
print("<br>");
}
sum(2, 4);
function multi($x, $y){ //return값이 있는 함수
return $x * $y;
}
file_put_contents('result.txt', multi(2, 4));
//file_put_contents('파일명', 삽입 내용 또는 변수);
//파일이 없다면 새로운 파일을 만들고, 있다면 내용을 덮어씌운다.
?>
</body>
</html>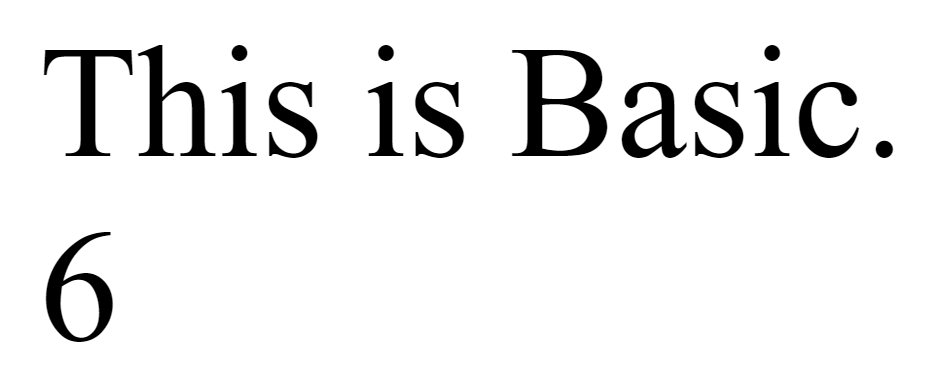

정보 시스템에서 해야할 일: How to ~
Create, Read, Update, Delete
폼(form)
- 사용자의 정보를 서버 쪽으로 전송할 때 사용하는 기능
<!--form.html-->
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
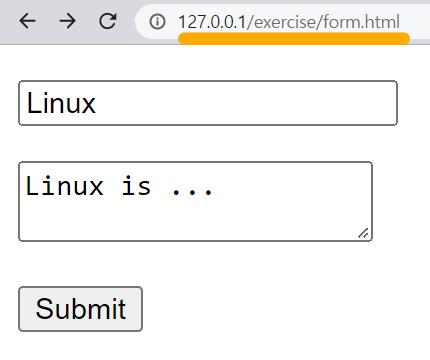
<form action="form.php"> <!--입력된 정보들을 가지고 form.php로 이동한다.-->
<p><input type="text" name="title" placeholder="Title"></p> <!--사용자로부터 text 정보를 입력받을 수 있다.-->
<p><textarea name="description"></textarea></p>
<p><input type="submit"></p>
</form>
</body>
</html>
<!--form.php-->
<?php
file_put_contents($_GET['title'], $_GET['description']); //title의 이름을 가진 파일에 description 내용을 저장
echo $_GET['title']; //title 출력
echo '<br>';
echo $_GET['description']; //description 출력
?>

- 데이터를 서버 쪽으로 전송할 때, url에 파라미터 정보가 포함되는 것은 좋지 않다.
- url을 클릭한 다른 사용자가, 이 url을 방문하면서 자신은 원하지 않았는데 글이 입력되는 심각한 문제가 발생할 수 있다.
- url을 통해 서버에 데이터를 전송하는 방식은 사용자가 서버로 데이터를 보낼 때 또는 어떤 데이터를 지울 때 사용하면 안 된다.
- url 파라미터를 통해서 서버에 데이터를 전송하는 것은, 북마크에서 사용하기 적합하다.
- url을 통하지 않도 다른 서버로 데이터를 전송하려면, <form> 태그에 method="post" 속성을 추가하고, $_GET[]을 $_POST[]로 바꾼다.
- method를 지정하지 않으면, 기본값은 "get"이다.
<!--form.html-->
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
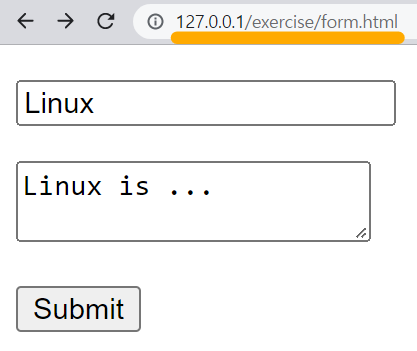
<form action="form.php" method="post">
<p><input type="text" name="title" placeholder="Title"></p>
<p><textarea name="description"></textarea></p>
<p><input type="submit"></p>
</form>
</body>
</html>
<!--form.php-->
<?php
file_put_contents($_POST['title'], $_POST['description']);
echo $_POST['title'];
echo '<br>';
echo $_POST['description'];
?>

form
생성하기(Create)
<!--index.php 내용 추가-->
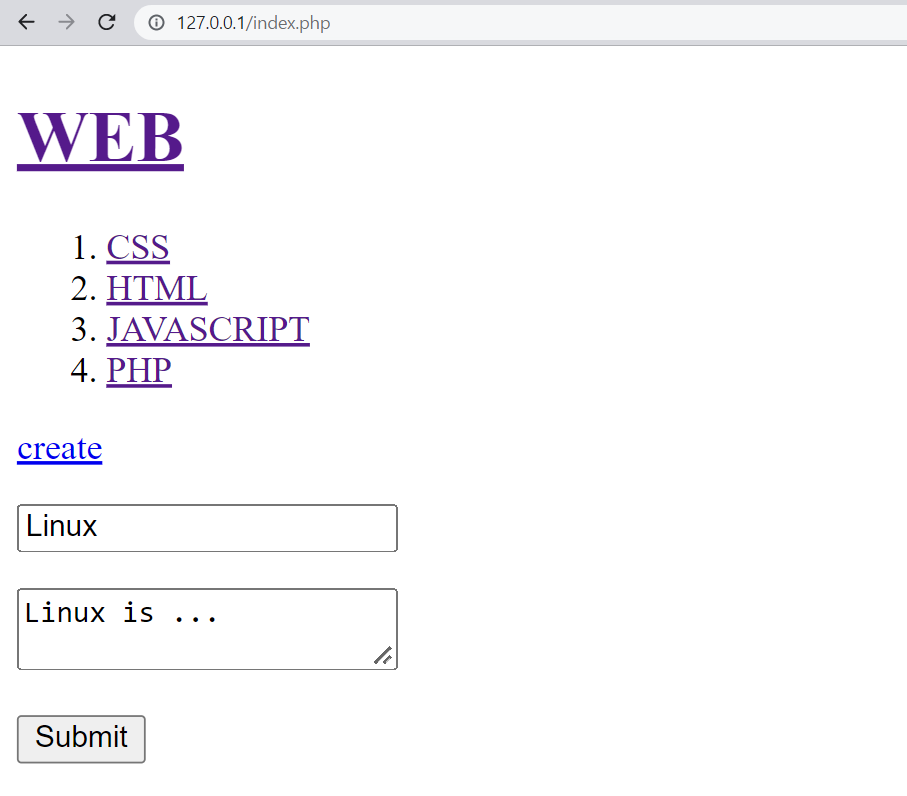
<a href="create.php">create</a>
<form action="create_process.php" method="post">
<p><input type="text" name="title" placeholder="Title"></p>
<p><textarea name="description" placeholder="Description"></textarea></p>
<p><input type="submit"></p>
</form>
<!--create_process.php-->
<?php
file_put_contents('data/'.$_POST['title'], $_POST['description']);
header('Location: /index.php?id='.$_POST['title']); //리다이렉션. 생성한 페이지로 이동된다.
?>

<?php echo ~~ ?>는 <?= ~~ ?>로 바꿀 수 있다.
수정하기(Update)
<!--update.php-->
<?php
function printTitle(){
if(isset($_GET['id'])){
echo $_GET['id'];
}
else{
echo "Welcome";
}
}
function printDescription(){
if(isset($_GET['id'])){
echo file_get_contents("data/".$_GET['id']);
}
else {
echo "Welcome to WEB";
}
}
function printList(){
$list = scandir('./data');
$i = 0;
while ($i < count($list)){
if ($list[$i] != '.'){
if ($list[$i] != '..'){
echo "<li><a href=\"index.php?id=$list[$i]\">$list[$i]</a></li>";
}
}
$i += 1;
}
}
?>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>
<?php
printTitle();
?>
</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1><a href="index.php">WEB</a></h1>
<ol>
<?php
printList();
?>
</ol>
<a href="create.php">create</a>
<?php if(isset($_GET['id'])){ ?> <!--id값이 있어야 <a href="update.php">update</a>가 뜬다.-->
<a href="update.php?id=<?= $_GET['id']; ?>">update</a>
<?php } ?>
<form action="update_process.php" method="post">
<input type="hidden" name="old_title" value="<?= $_GET['id'] ?>"> <!--웹페이지 사용자의 눈에는 보이지 않으면서, 데이터를 form이 지정한 사이트에 보내고 싶을 때, type="hidden"을 사용한다.-->
<p><input type="text" name="title" placeholder="Title" value="<?php printTitle(); ?>"></p>
<p><textarea name="description" placeholder="Description"><?php printDescription(); ?></textarea></p>
<p><input type="submit"></p>
</form>
</body>
</html><!--update_process.php-->
<?php
rename('data/'.$_POST['old_title'], 'data/'.$_POST['title']); //파일 이름 변경
file_put_contents('data/'.$_POST['title'], $_POST['description']); //내용 변경
header('Location: /index.php?id='.$_POST['title']); //리다이렉션. 생성한 페이지로 이동된다.
?>


삭제하기(Delete)
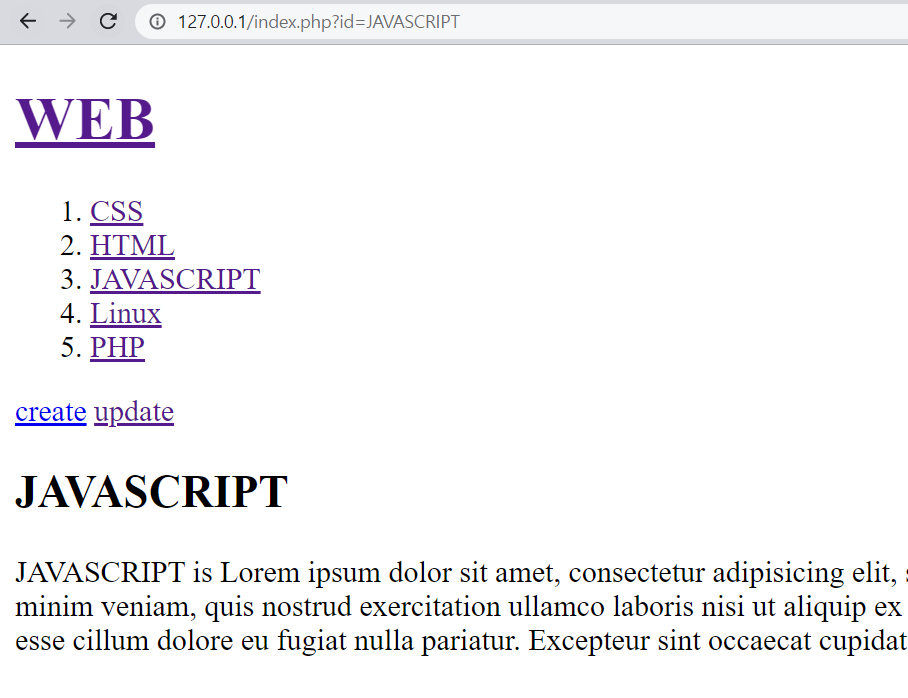
<!--index.php-->
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>
<?php
printTitle();
?>
</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1><a href="index.php">WEB</a></h1>
<ol>
<?php
printList();
?>
</ol>
<a href="create.php">create</a>
<?php if(isset($_GET['id'])){ ?> <!--id값이 있어야 <a href="update.php">update</a>가 뜬다.-->
<a href="update.php?id=<?= $_GET['id']; ?>">update</a> <!--delete는 form을 거칠 필요 없이, 바로 삭제할 수 있다.-->
<form action="delete_process.php" method="post">
<input type="hidden" name="id" value="<?=$_GET['id']?>">
<input type="submit" value="delete">
</form>
<?php } ?>
<h2>
<?php
printTitle();
?>
</h2>
<?php
printDescription();
?>
</body>
</html>
<!--delete_process.php-->
<?php
unlink('data/'.$_POST['id']); //페이지 삭제
header('Location: /index.php'); //홈으로 이동
?>

리팩토링하기 - 중복되는 부분 최대한 줄이기

require('파일이름')
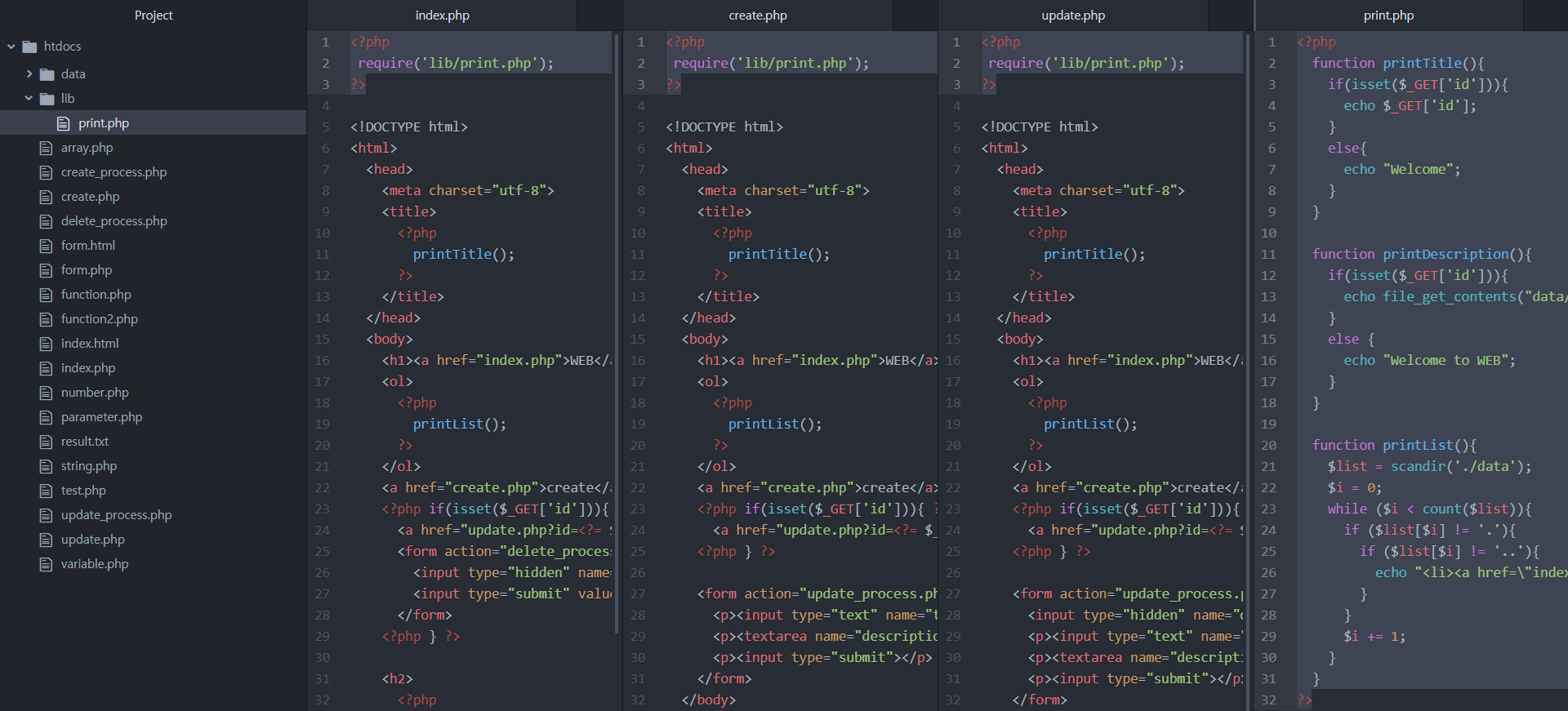

require_once
- redeclare를 무시한다.

top.php의 printTitle 함수는 lib/print.php에 정의되어 있다. printTitle 함수가 어디에서 왔는지 명확히 해주기 위해 require('lib/print.php);를 하면, index.php, create.php, update.php 에서는 view/top.php 파일을 호출하기 이전에 이미 lib/print.php를 호출했기 때문에 declare가 두 번 일어나게 된다. require_once 함수는 오류를 발생시키는 redeclare를 방지하기 위해, 한 번 declare된 파일이 다시 declare되면 무시한다.
Cross Site Scripting(XSS)




XSS를 방지하기 위한 php 함수: htmlspecialchars
- 특정 특수문자를 html 엔티티로 변환한다.
<!--xss.php-->
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<?php
echo htmlspecialchars('<script>alert("babo");</script>');
?>
</body>
</html>
basename
- 파일 경로에서 파일명만 출력하는 함수
Inspect - Network: Preserve log를 체크하면 서버랑 주고받는 정보들을 쌓아둘 수 있다.

<!--delete_process.php-->
<?php
unlink('data/'.basename($_POST['id'])); //basename 함수로 경로가 드러나지 않게 한다.
header('Location: /index.php');
?>
UI(User Interface) VS API(Application Programming Interface)
API: 태그, 함수 등. 언어의 부품들.
https://www.php.net/manual/en/funcref.php
PHP: Function Reference - Manual
www.php.net
Composer
A Dependency Manager for PHP Latest: 2.3.10 (changelog) Getting Started Download Documentation Browse Packages Issues GitHub
getcomposer.org
- Browse Packages - Browse: 필요한 패키지들을 사용할 수 있음
파일의 대체제: 데이터베이스. 데이터를 훨씬 더 체계적이고 안전하고 빠르게 관리할 수 있다.
성능을 높이려면, 정보가 생성될 때마다 사용자가 검색할법한 정보의 위치를 미리 어딘가에 적어둔다.
php cookies, php session: 사용자 관리 기능
facebook, google 등 대기업의 인증절차를 빌려 로그인하는 경우(타사 인증, federation authentication)
- 버튼 한 번 또는 몇 번으로 간편하게 로그인 가능, 회원에 대한 중요한 정보를 최소한으로 가지고 있을 수 있다. 나쁜 점은, 종속된다는 것이다.
'웹기초 > 생활코딩 WEB 2 - PHP' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [웹기초] 생활코딩 PHP 9 ~ PHP 17 (0) | 2022.07.11 |
|---|---|
| [웹기초] 생활코딩 PHP 4 ~ PHP 8 (0) | 2022.07.11 |
| [웹기초] 생활코딩 PHP 1 ~ PHP 3 (0) | 2022.07.11 |



